Understanding Bypass Surgery: A Comprehensive Guide
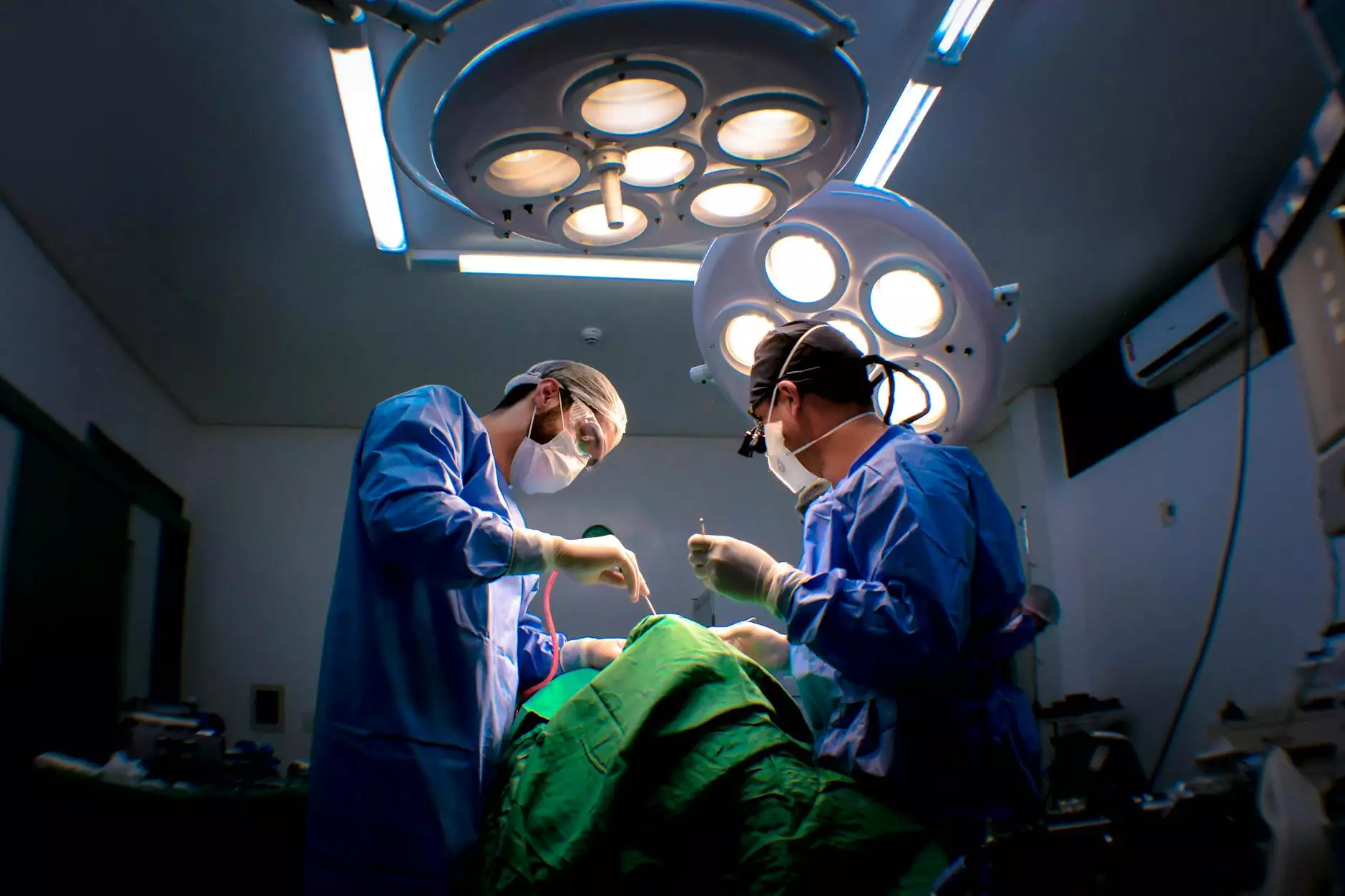
Bypass surgery, commonly referred to as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), is an important medical procedure designed to improve blood flow to the heart. This article aims to provide a thorough understanding of bypass surgery, how it works, its benefits, and the overall impact on health and wellness.
What is Bypass Surgery?
Bypass surgery is a surgical procedure that involves creating a new pathway for blood to flow to the heart. This is achieved by taking a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body, such as the leg, arm, or chest, and attaching it to the coronary arteries to bypass narrows or blockages that impede blood flow.
Why is Bypass Surgery Necessary?
The primary reason for performing bypass surgery is to treat coronary artery disease (CAD). This condition arises when the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked by cholesterol and fatty deposits, known as plaque. Some common symptoms of CAD that may lead to the consideration of bypass surgery include:
- Chest Pain (Angina): Discomfort or pain in the chest during physical activity or emotional stress.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially when exerting oneself.
- Fatigue: Unusual tiredness, particularly after exertion.
How is Bypass Surgery Performed?
The procedure typically involves the following steps:
1. Preoperative Preparations
Before the surgery, patients undergo a series of tests, including blood tests, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and imaging studies to determine heart function and evaluate overall health status.
2. Anesthesia
The patient is given general anesthesia to ensure they are asleep during the procedure. This guarantees that the patient feels no pain and is completely unaware of the surgical process.
3. The Surgical Procedure
The surgeon will make an incision down the middle of the chest, which involves dividing the breastbone to access the heart. Following this, a healthy blood vessel is harvested for the graft. In many instances, the internal thoracic artery, saphenous vein from the leg, or radial artery from the arm may be used.
4. Grafting
Once the graft is prepared, the surgeon will attach one end to the aorta and the other to the coronary artery, bypassing the blocked section. Multiple grafts may be performed if necessary, restoring blood flow to various areas of the heart.
5. Closing the Chest
After the grafting is completed, the surgeon will carefully close the chest cavity, using sutures or staples to ensure the incision heals properly.
Benefits of Bypass Surgery
Bypass surgery offers numerous benefits to patients suffering from severely narrowed or blocked arteries:
- Improved Blood Flow: Bypass surgery allows for increased blood flow to the heart, consequently reducing or eliminating symptoms of CAD.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Many patients report substantial improvements in their overall quality of life, experiencing less chest pain and increased exercise tolerance.
- Increased Lifespan: Studies have shown that bypass surgery can prolong the lives of individuals with significant coronary artery disease.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery period following bypass surgery is critical and typically involves several phases:
1. Hospital Recovery
Patients usually stay in the hospital for about 3 to 7 days after surgery, where they undergo monitoring for complications and begin initial stages of recovery.
2. Home Recovery
Once discharged, resting at home allows the body to heal. It is vital to follow the doctor’s recommendations for care, including gradually reintroducing physical activity.
3. Cardiac Rehabilitation
A structured cardiac rehabilitation program is often advised to help patients safely regain strength, confidence, and endurance. Such programs often include:
- Supervised exercise training
- Nutritional counseling
- Support for lifestyle changes
Potential Risks of Bypass Surgery
As with any major surgery, bypass surgery carries potential risks. These include:
- Bleeding: Excessive blood loss during or after surgery may require additional medical intervention.
- Infection: Surgical site infections can occur, requiring further treatment.
- Heart Complications: Abnormal heart rhythms or heart attack may occur during or after surgery.
What to Expect After Bypass Surgery
Post-surgery, the lifestyle changes are paramount for maintaining heart health. Here are a few essential changes to consider:
- Dietary Adjustments: Emphasize a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activity that enhances cardiovascular strength, as advised by the cardiologist.
- Medication Compliance: Adhere to prescribed medications to prevent blood clots and manage cholesterol levels.
When to Consult a Doctor
Individuals should consult healthcare professionals if they experience:
- Severe Chest Pain: Sudden and intense chest pain could be a warning sign.
- New Symptoms: Onset of symptoms such as persistent fatigue or increased breathlessness.
- Postoperative Issues: Signs of infection, unusual swelling, or changes in medication response.
Conclusion
Bypass surgery is a critical intervention for patients with significant coronary artery disease, offering improved blood flow and quality of life. While the surgery itself entails various stages and risks, the benefits often outweigh the potential complications. It’s essential to embrace a heart-healthy lifestyle post-surgery to ensure long-lasting health and well-being.
For further insights on bypass surgery and other health concerns, feel free to explore resources and connect with healthcare providers specializing in this field.
Remember: informed decisions contribute significantly to successful outcomes.